What if you could design a house that used absolutely no energy. In fact, what if it was so sustainable it produced a surplus.
This ‘what-if’ was at the heart of architecture and design firm Snøhetta’s intent behind the ZEB Pilot House. Snøhetta, who’s credited with such insane projects as the first underwater restaurant in Norway, the SFMOMA Expansion, a NYC Time Square revision, and Oslo’s 2022 Olympic Games bid, Collaborated on ZEB Pilot House with Scandinavia’s largest independent research body SINTEF, Zero Emission Building (ZEB) partner Brødrene Dahl, and Optimera, to create a house that is 100% sustainable yet livable.
The house, although built in the style of a single-family residence, will not be inhabited any time soon (the build was completed in 2014), as ZEB Pilot will act as just that— a model home demonstrating the ability of sustainable solutions and “plus dwellings,” which are buildings that produce more energy than they use.
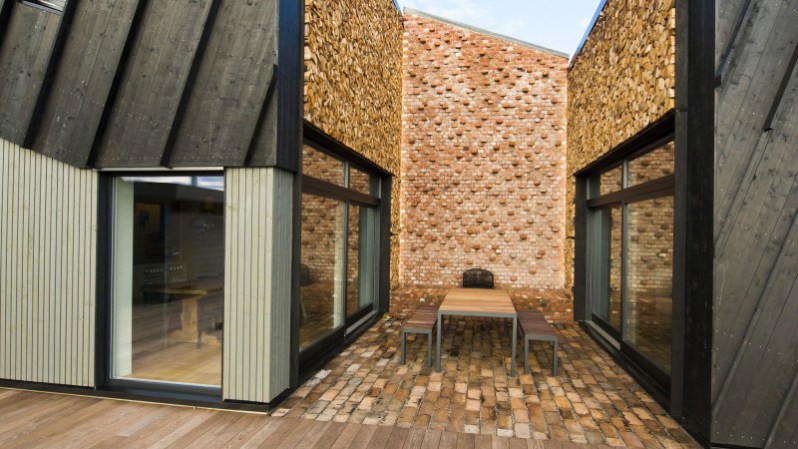

At first glance, ZEB Pilot reveals itself as a simple, modernist home (check out another stunner here), utilizing an asymmetrical slanting roof, cut-out patio, simple outdoor stone pool, and plenty of texture play between wood, stone, and steel. Sure, judge this book by its cover (because the cover is gorgeous and understated), but don’t stop there.
Beneath the hood of ZEB Pilot is a matrix of energy-efficient solutions you’d never dream of, from unique indoor wood sealing that promotes heat retention to strategic glass window placement. In fact, nearly every geometric slice of the home’s foundation, the materials used, and the houses’s placement contribute to a good indoor climate, air quality, and thermal prowess.
The gleaming jewel of ZEB Pilot’s sustainable superiority is on the roof, where solar panels and collectors slope southeast for optimal sunlight. On the ground level, geothermal energy wells are dug under the earth, a rainwater collector is positioned to flush the toilet and water the garden, and ZEB Pilot is even smart enough to automatically control light and air based on use and need. Think of it as a smart thermostat that can predict when you’re home and gone, adjusting the temperature and energy-spend on its own. (Dad’s everywhere are stunned.)
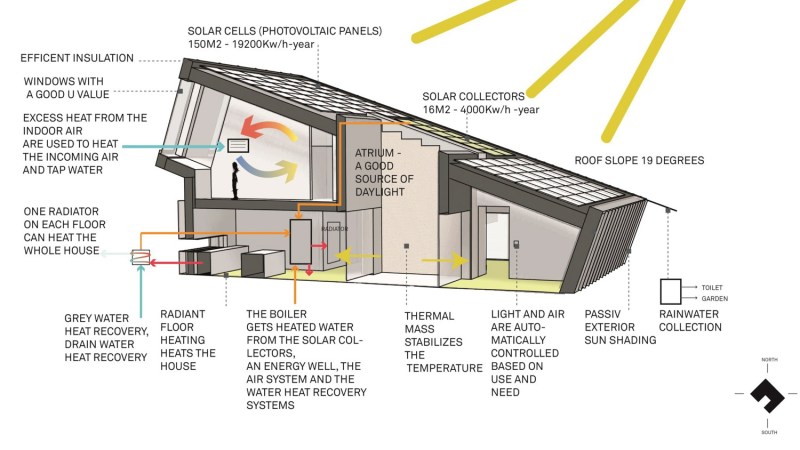
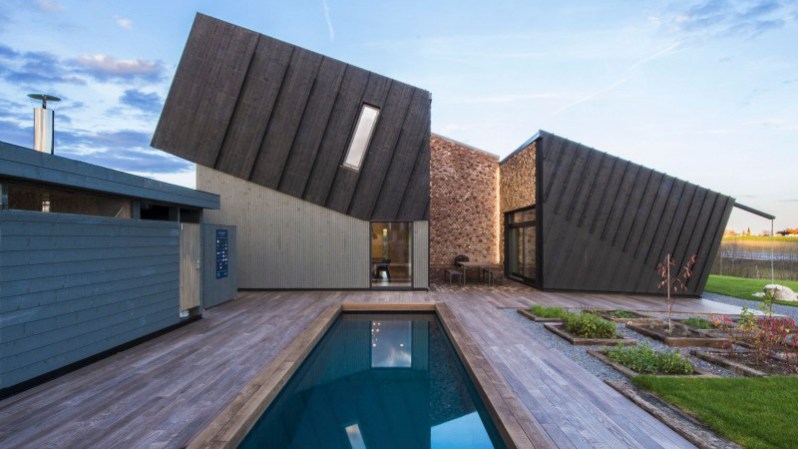
But despite its panels and material placements, ZEB Pilot is nonetheless made to be a livable, warm, comfortable house. The overall design has a focus on, “retaining home-like qualities,” such as “emotive comfort and sense of well-being,” says designers at Snøhetta. And indeed, ZEB Pilot evokes that close, comforting sensation, with a social outdoor atrium with fireplace and walls of stacked wood surrounding the section, a small garden, and solar-heated family pool overlooking the landscape.
As for its name: ZEB, the house takes on this title with its achievement of ZEB-OM classification, which means the project is required to document and verify a minimum of 100% CO2 offsetting. And not just while it’s running, but as it was being built. All energy expenditure that went into ZEB was offset by its own, sustainable production, or in fancy terms, as Snøhetta puts it:
“Renewable energy production via photovoltaic and solar-thermal panels integrated in the building envelope enables offsetting of carbon emissions generated by the burning of fossil fuels in power stations. By offsetting in this manner, we reduce emission of other greenhouse gasses simultaneously. Focus on carbon emissions associated with building materials represents a new direction in the vital drive toward a sustainable construction industry. New tools are put to use, the academic disciplines work closer together, and the requirements for documentation are more demanding than ever. In particular, the high focus on choice of material in early development phases is new, and it generates innovative design processes on a multidisciplinary level.”

The element of recording and research for ZEB Pilot mean the house will never be occupied by a real, living family (why are we tearing up… it’s a house). However, it also means that as time passes and the weather changes and materials naturally age, we’ll have hard data on how the most sustainable living and design components will stand the test of time; which could lead to smarter houses, better living, and a healthier world.
That, my friends, is the best news we’ve heard all 2017.


