Treadmills, ellipticals, and exercise bikes are often many people’s go-tos when it comes to cardio equipment. While these machines can certainly be effective, what about the benefits of rowing? Rowing allows you to strengthen your upper body, especially your back, while still challenging your cardiovascular system.
If you’re feeling stuck in a rut with your current fitness routine or are interested in taking on the most efficient and effective ways to get in shape, keep reading for a list of the benefits of rowing. Even if you’ve been hesitant to give rowing a try, you may just find yourself rethinking your next workout and swapping your run or spin class for a workout on the rowing machine.

Benefits of rowing
The benefits of rowing are extensive, spanning the gamut from improving cardiovascular
Rowing improves cardiovascular health and fitness
Rowing is an excellent aerobic workout. You’ll get your heart rate elevated and find yourself breathing heavier within just a few minutes. In this way, rowing improves your cardiovascular health and
Rowing is a total-body workout
Although many people imagine rowing to be an upper-body exercise, most of the power for the rowing stroke actually comes from your legs. In fact, when looking at the rowing stroke, 60% of the work should be done by the legs, 30% from the core, and just 10% from the upper body. Moreover, studies investigating the muscular recruitment patterns with rowing have found that rowing uses roughly 86% of the muscles in your body, making it a fantastic total-body workout. Rowing strengthens your quads, glutes, core, lats, shoulders, hamstrings, biceps, and calves.

Rowing burns a lot of calories
One of the benefits of total-body workouts like rowing is that they burn a lot of calories. By using most of the major muscles in your body, rowing requires a lot of energy and makes for an efficient calorie burn. Additionally, a rowing machine is a great way to get in a challenging high-intensity interval training (HIIT) workout, which stokes your metabolism and helps your body burn more calories even once you’re done exercising. Try rowing relatively easily for a few minutes to warm up, and then push yourself through hard intervals of 30 to 90 seconds, followed by easy recovery rows.
Rowing is a time-efficient way to exercise
Most of us are super busy these days and don’t have an endless amount of time to dedicate to working out. Therefore, efficiency when it comes to exercise is key. Another benefit of rowing is that it can provide a cardio and strength training workout simultaneously, saving you time when you have lots of things on your plate. A vigorous 20-minute workout on a rowing machine can be enough to improve your
Rowing is a low-impact activity
If you suffer from joint pain, arthritis, or chronic musculoskeletal injuries, rowing may be exactly what you are looking for when it comes to a joint-friendly form of exercise. Rowing is considered a low-impact exercise, like cycling, elliptical trainers, and swimming, so it puts less stress on your joints, bones, and connective tissues than running, jumping, and other high-impact sports. As long as you’re using proper form, the risk of injury on a rowing machine is also very low.
Rowing is calming
Rowing can be quite meditative, and many people find that rowing is a great way to reduce anxiety and induce a sense of peace. The stroke is rhythmic and repetitive, but not in a boring way. Like other forms of exercise, rowing also produces endorphins, the feel-good chemicals that elevate your mood, so you’ll leave your workout feeling happier, calmer, and more confident.
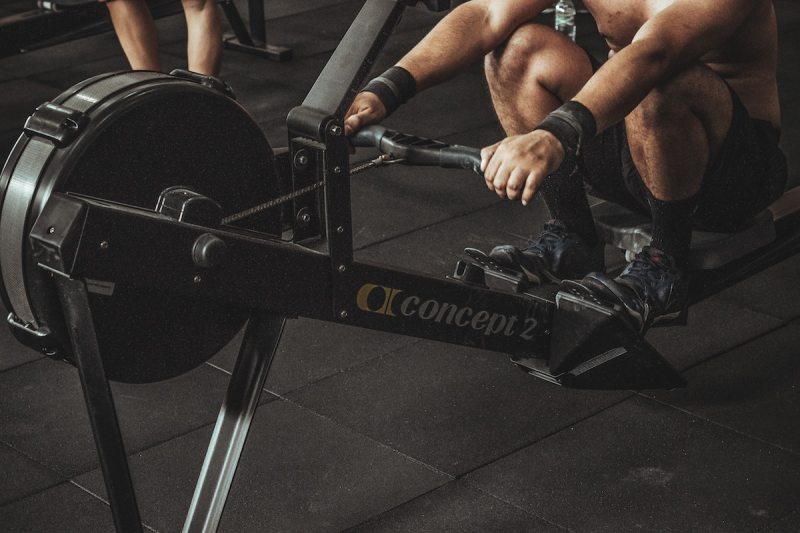
Rowing can improve your posture and core strength
The rowing stroke relies heavily on core activation and control, so it can help you build core strength and improve your posture over time. A strong core can reduce the incidence of low back pain and help prevent injuries. Plus, because good form is crucial with rowing, it’s also a good way to increase your mind-body connection and kinesthetic awareness.
Rowing is motivating
If you’re using a rowing machine, it’s easy to keep track of your metrics and watch how much you’re improving over time. Because rowing is a learned skill, most beginners get to experience significant improvements quickly, which is really motivating. Even if you’ve been using a rowing machine for years, you can continue to challenge yourself and play games in your workouts to see if you can hit new milestones and personal bests, which can keep your mind engaged.

A breakdown of the muscles used in rowing
As mentioned above, rowing is a total-body exercise that works at least 86% of the muscles in the body. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of how each muscle group is used during the rowing stroke:
Lower body
- Quadriceps: The quads extend the legs at the knee during the drive phase of the rowing stroke.
- Hamstrings: The hamstrings flex the hips and extend the legs at the knee during the finish phase of the rowing stroke.
- Glutes: The glutes extend the hips during the drive phase of the rowing stroke.
- Calves: The calves plantarflex the ankle during the recovery phase of the rowing stroke.
Upper body
- Latissimus dorsi (lats): The lats pull the torso forward during the drive phase of the rowing stroke.
- Trapezius: The trapezius stabilizes the shoulder girdle during the rowing stroke.
- Deltoids: The deltoids pull the handle toward the chest during the finish phase of the rowing stroke.
- Biceps: The biceps supinate the forearm during the finish phase of the rowing stroke.
- Triceps: The triceps extend the elbow during the recovery phase of the rowing stroke.
Core
- Abdominals: The abdominals stabilize the spine and pelvis during the rowing stroke.
- Obliques: The obliques rotate the torso during the rowing stroke.
- Erector spinae: The erector spinae extends the spine during the recovery phase of the rowing stroke.



