Hair loss is one the biggest fears among all men, affecting up to 70% of them. If you research hair loss, you will eventually come across the importance of biotin, which is one of the B vitamins. Studies have shown biotin’s ability to increase hair strength, thickness, and growth. Biotin also improves the health of nails and performs other critical functions in the body. For example, biotin plays a crucial role in specific metabolic and energy-generating pathways by helping break down carbs, proteins, and fats into usable energy. Biotin also helps regulate blood sugar, supports healthy skin, and assists in cell signaling.
Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin, meaning the body cannot store significant amounts, therefore it must be consumed regularly in the diet. The recommended daily intake (RDA) of biotin for most adults is 30 to 100 mcg. While supplements are always an option, it’s better to get you micronutrients through diet. Luckily, there are plenty of foods high in biotin. Consuming a variety of biotin-rich foods will help ensure adequate intake to support a healthy metabolism, energy generation, a full head of hair, and youthful skin. With that in mind, here are some of the foods high in biotin to help you maintain your luscious locks.
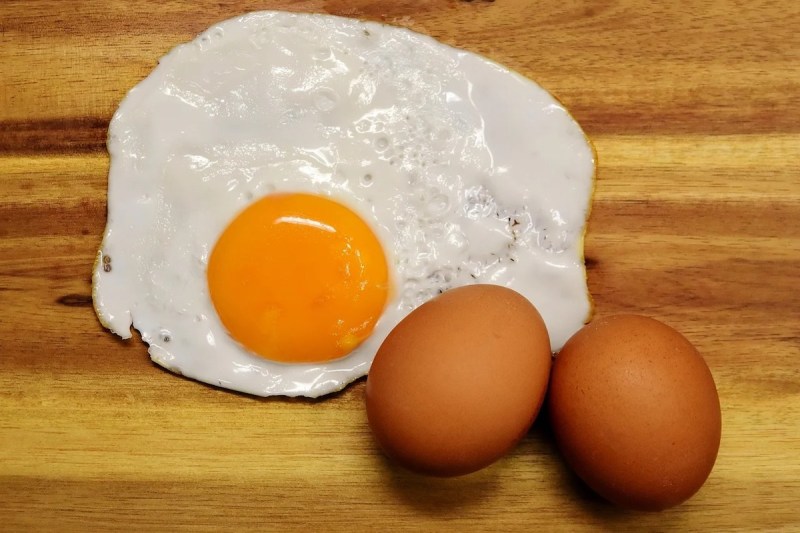
Egg yolks
Eggs are one of nature’s little packages of vital nutrients. For example, an egg is a complete source of protein, meaning it contains all essential amino acids. Egg yolks are also rich in vitamin D, a fat-soluble vitamin that plays important roles in bone health, along with iron, which helps transport oxygen in the blood to every cell and tissue in the body. Egg yolks are also rich in B vitamins, especially biotin, with 10 mcg of biotin (33% DV) per whole egg. It’s important to note that eggs must be cooked to capitalize on this biotin, as raw egg whites contain avidin, a protein that interferes with biotin absorption.

Salmon
Salmon and other fatty fish are revered for their high omega-3 fatty acid content, which helps reduce inflammation in the body. Salmon is also a great source of biotin, with each 3-ounce serving of cooked salmon providing 5 mcg of biotin. Because salmon also contains healthy fats, it’s an excellent food for healthy skin and hair.

Yeast
Brewer’s yeast, which is used to make bread and beer, contains a decent amount of biotin, as does nutritional yeast, a product used in many vegan cheeses and non-dairy substitutes. There is 21 mcg in every 2-tablespoon serving of nutritional yeast, for example. If you’re not sure how to use it, think of it somewhat like a Parmesan cheese substitute. Sprinkle it on salads, pasta dishes, soups, or even popcorn.

Meat
If you love the carnivorous part of your diet, you’re in luck. Meats such as hamburgers and pork chops are rich sources of biotin. A 3-ounce serving of either contains 13% of the DV, or 3.8 mcg, of biotin. Opt for lean meats to maximize the health benefits.

Legumes
The majority of legumes, such as beans, lentils, peanuts, and soybeans, are a great source of biotin. They also provide complex carbohydrates, plenty of fiber, prebiotics, and iron. Peanuts and soybeans contain the most biotin among this group. For example, a 1-ounce (28 grams) serving of roasted peanuts contains nearly 5 mcg of biotin, which is 17% of the recommended daily value. When considering soybeans, there is a whopping 19.3 mcg of biotin (64% DV) per 3/4 cup.

Liver
Although it’s not everyone’s cup of tea, liver is one of the best dietary sources of biotin because biotin is stored in the liver (in limited quantities since it’s a water-soluble vitamin). Cooked chicken liver is an extremely rich source of biotin, with an impressive 138 mcg per 3-ounce serving, which is equivalent to 460% of the DV. Cooked beef liver is a slightly less potent source of biotin, but still provides 31 mcg (103% DV) per 3-ounce serving. Liver can take some getting used to, with a prominent metallic flavor due to its high iron content. However, its nutritional benefits are enough to win over some initially reluctant eaters, so you might consider giving it a try.

Sunflower seeds
Many people consider seeds to be superfoods, as they provide an array of key vitamins, minerals, and essential fats. Hemp seeds, for example, also provide a lot of fiber, and minerals such as calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, zinc, and copper. Moreover, they are a rich source of biotin. Another good option for seed lovers is sunflower seeds, with each 1/4 cup (20 grams) serving of roasted sunflower seeds providing 2.6 micrograms of biotin, which is roughly 10% of the recommended daily value.
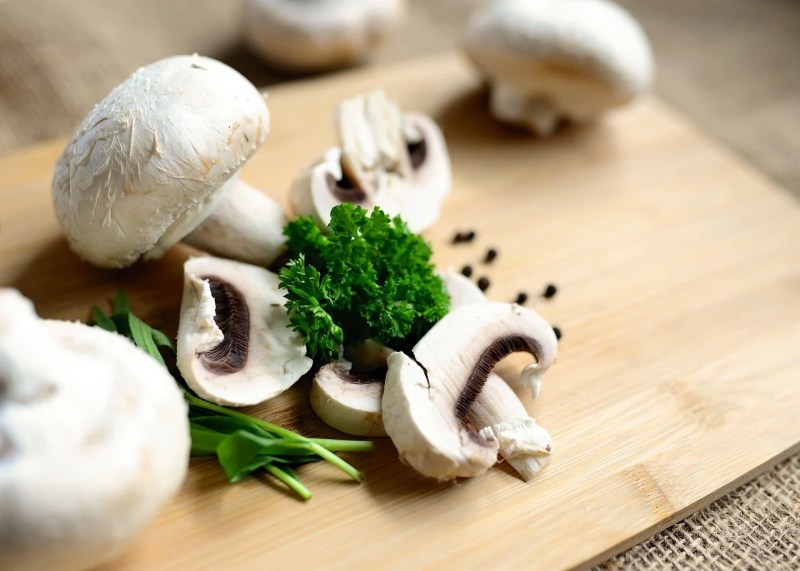

Mushrooms
Mushrooms provide you with antioxidants along with minerals like selenium and magnesium. They also contain biotin, with each cup of fresh button mushrooms providing 5.6 mcg. Consider adding mushrooms to salads, stir-fries, sandwiches, or hearty winter soups.
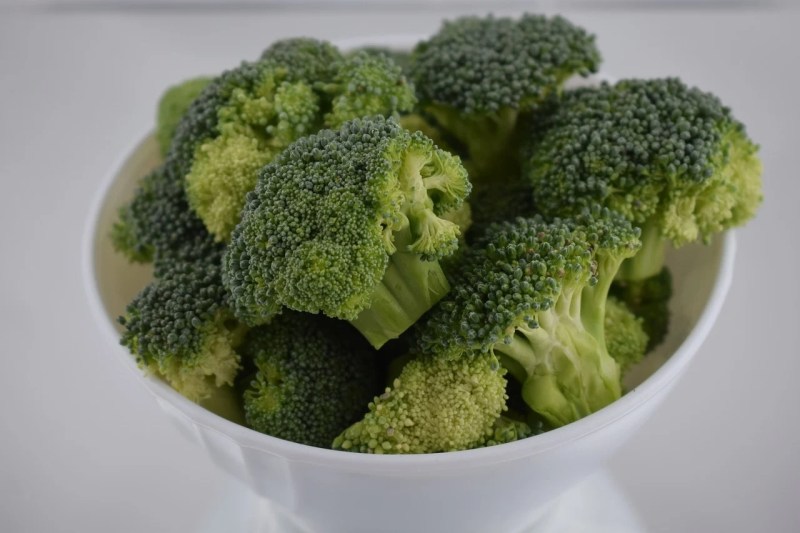

Broccoli
Though the biotin content in broccoli is fairly low — at 0.4 micrograms per half-cup — it’s such a powerhouse of other key nutrients like vitamin C, fiber, water, and calcium, that it never hurts to add it to your plate.
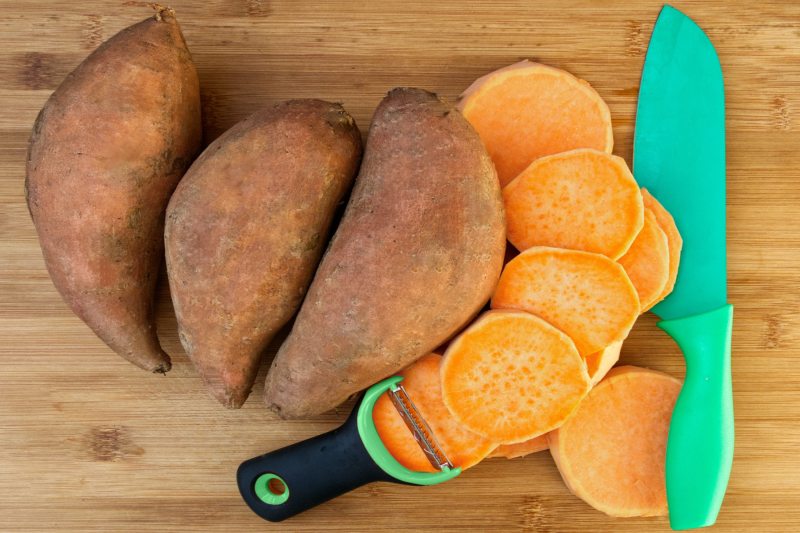

Sweet potatoes
Sweet potatoes are packed with nutrients such as vitamin A and beta-carotene, vitamin C, fiber, manganese, potassium, copper, and magnesium. They are also one of the best vegetable sources of biotin. There is 2.4 mcg (8% of the recommended daily value) of biotin per 1/2 cup of cooked sweet potato. Along with the vitamin A in sweet potatoes, which is also good for the eyes and skin, the biotin makes sweet potatoes a superfood for skin health. Enjoy sweet potatoes baked, microwaved, steamed, roasted, mashed, spiralized, grilled, or even riced. If you prefer less starchy root vegetables, carrots also contain a decent amount of biotin and plenty of vitamin A as well.
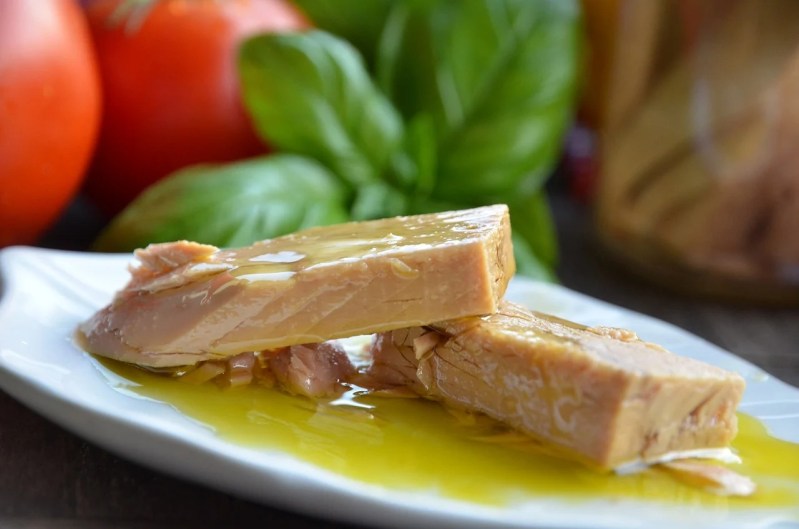

Tuna fish
Canned tuna is inexpensive and convenient. Moreover, it’s a good source of biotin. A 3-ounce can of tuna packed in water provides 0.6 micrograms of biotin. Canned tuna also provides nutrients like tryptophan, which can aid sleep and promote the production of serotonin, a feel-good neurotransmitter that elevates mood.

Almonds
Almonds are a good source of biotin, with 1.5 mcg per quarter cup. Almonds also provide healthy monounsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation and support heart health. They also contain vitamin E, another essential nutrient for hair and skin health. To boost your biotin dose, consider pairing almonds with another biotin-rich food, such as oatmeal. If you prefer to go the trail mix route, combine almonds with peanuts, which provide about 0.8 mcg per serving.

Spinach
There are many health benefits to eating your leafy greens. From fiber and foods high in vitamin C to polyphenols and antioxidants, spinach is chock full of essential nutrients. It also provides 0.5 mcg of biotin per 1/2 cup of cooked spinach.

Cheese and other dairy
Cheddar cheese is the best dairy source of biotin, with 0.4 mcg per 1-ounce serving. Milk and plain yogurt are also good sources. Foods with melatonin, such as milk can help regulate your sleep cycle to keep you from tossing and turning at night.
How do I know if I have a biotin deficiency?
Biotin deficiencies are extremely uncommon, so it’s likely that you don’t have to worry about this. The foods we listed above are in most people’s regular diet, making hitting your daily biotin goals rather effortless.
However, there is nothing wrong with keeping an eye out for any nutrient deficiency, including biotin. If you experience the following symptoms, your diet may be lacking in biotin.
- Dry skin
- Cracking around the corners of the mouth
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Thinning hair or hair loss
- Red rash around openings, such as the eyes, nose, and mouth
Tasty food for thicker hair
With 14 different appetizing food options brimming with substantial biotin content, there is sure to be an option that can fit anyone’s palatable preference, regardless of dietary restrictions. The hardest part will be in choosing only one.




