Embarking on a journey towards better health and weight loss often starts with the simplest advice: eat your greens. Yet, the world of lettuce is far from a uniform sea of foliage. It’s a nuanced tapestry of nutritional variety, and not all lettuce varieties are created equal.
Here, we’ll decipher the science behind Romaine lettuce, Iceberg lettuce, and their leafy relatives, revealing the healthiest option. This article will help you make informed choices about your bowl of greens.

How many types of lettuce are there?
Venturing into the world of lettuce is a journey that transcends the seemingly uniform sea of greens, revealing a botanical landscape rich in diversity. It’s crucial to understand that while all lettuce are greens, not all greens are lettuce. Let’s unravel the intricacies and distinctions within this verdant realm.
The term “greens” is a broad category encompassing various leafy vegetables that are typically consumed in salads or cooked dishes. It includes a spectrum of vegetables such as kale, spinach, arugula, Swiss chard, and more. These greens boast diverse flavors, textures, and nutritional profiles.
On the other hand, “lettuce” refers specifically to a subset of greens belonging to the Lactuca sativa species. Lettuce varieties, including Iceberg, Romaine, Butterhead, and others, share a common lineage but exhibit distinct characteristics, tastes, and nutrient compositions.
Iceberg lettuce
Known for its crisp texture and mild flavor, Iceberg lettuce may have a reputation for being low in nutrients, but it does provide hydration and some essential vitamins. While it may have earned a reputation for being nutrient-light compared to its leafy counterparts, this crisp and refreshing variety brings some surprising health benefits to the table.
Rich in vitamins A and K, Iceberg lettuce delivers a substantial nutrient boost. Vitamin A plays a crucial role in supporting vision and immune function, while vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health.
Romaine lettuce
Romaine lettuce contributes to your body’s antioxidant defenses. Antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and supporting cellular health. The combination of vitamins and minerals, coupled with various phytonutrients present in Romaine lettuce, creates a robust antioxidant arsenal that may contribute to overall well-being.
In the bustling landscape of superfoods vying for attention, romaine lettuce quietly emerges as a nutritional gem, quietly awaiting its moment in the dietary spotlight. Beyond its customary role as a salad foundation, romaine lettuce, with its unassuming appearance, houses a diverse array of health benefits. This nutritional revelation extends from omega-3 fatty acids, recognized for their anti-inflammatory prowess, to the plant-based protein fostering muscle health. Romaine lettuce emerges not just as a salad component but as a versatile and crucial addition to a well-rounded diet.
Dark leafy greens
Dark leafy greens, such as spinach, kale, and arugula, stand as nutritional powerhouses, distinct from traditional lettuces. Their deep green hues signify a rich concentration of essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, and K, which play pivotal roles in immune support, vision, and bone health. Unlike the milder taste and lighter texture of lettuce, these greens carry a robust and often peppery flavor, adding complexity to dishes.
Their antioxidant content is higher, contributing to a more potent defense against oxidative stress and potential protection against chronic diseases. The notable presence of dietary fiber in dark leafy greens sets them apart, promoting digestive health, regulating blood sugar, and aiding in weight management.
Additionally, the iron content in these greens supports oxygen transport, fostering sustained energy levels. By incorporating spinach, kale, and arugula into your diet, you not only introduce a burst of flavor but also harness a diverse nutrient profile that goes beyond the familiar realm of lettuce, enhancing your overall well-being.
Butterhead (or Bibb) lettuce
Butter lettuce, also known as Bibb lettuce or Boston lettuce, is a delightful leafy green characterized by loose, tender leaves that form a round or semi-rounded head. Its unique appeal lies in its soft, buttery texture and mild, slightly sweet flavor, making it a favored choice for salads and sandwiches alike.
Beyond its culinary attributes, butter lettuce offers notable health benefits. Rich in essential vitamins, particularly vitamin A, it supports vision and immune function. Moreover, with a low-calorie count, it is a valuable option for those aiming to manage their weight while providing hydration through its high water content. Though not as fiber-rich as some other lettuce varieties, butter lettuce contributes to digestive health and satiety.
The presence of antioxidants in butter lettuce may also assist in combating oxidative stress and inflammation, contributing to overall well-being. While appreciating the unique taste and texture of butter lettuce, incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into a well-rounded diet remains key to holistic health.
Red and green leaf lettuce
Red and green leaf lettuce, vibrant and visually appealing members of the lettuce family, not only add color to your plate but also contribute essential nutrients to your diet. Red leaf lettuce, with its distinctive bold color, brings not only aesthetic pleasure but also a mix of antioxidants, potentially offering health benefits by combating oxidative stress. On the other hand, green leaf lettuce shares the tender characteristics of its red counterpart but introduces a milder flavor profile, making it a delightful addition to a wide range of dishes.
What sets green leaf lettuce apart is its role as a good source of essential vitamins A and K, supporting vision, immune function, and bone health. Both red and green leaf lettuce varieties share the advantage of being low in calories, making them excellent choices for those mindful of weight management or seeking a healthy diet. Additionally, with their high water content, these lettuce varieties contribute to overall hydration, promoting not only a colorful and flavorful culinary experience but also supporting skin health and general well-being.

So, which one is the healthiest?
Understanding the distinctions between these lettuce types allows you to make informed choices when creating your salads, ensuring that your culinary preferences align with your nutritional goals. We can now unravel the mystery of which lettuce variety is the healthiest.
As one of the healthiest lettuce varieties, romaine lettuce stands out from its competitors. A darker, elongated leaf makes romaine lettuce a superior nutritional source. Even when compared to dark leafy greens like spinach, kale, and arugula, romaine lettuce delivers a unique combination of vitamins and minerals. In addition to its hydrating and crunchy nature, romaine lettuce provides a noteworthy boost in vital nutrients while enhancing the culinary experience.
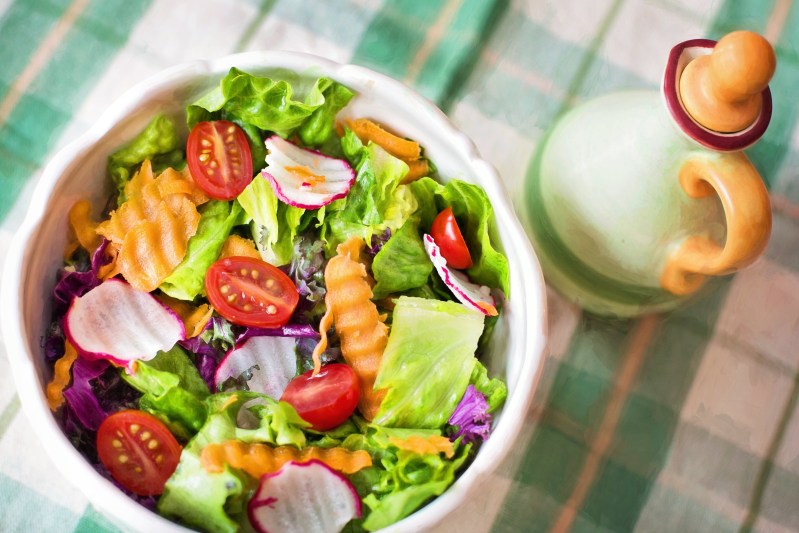
How to get more lettuce into your diet
Incorporating more romaine lettuce into your daily diet is a simple and delectable strategy to enhance your overall nutritional intake.
- Consider substituting traditional iceberg lettuce with the darker, more nutrient-rich romaine leaves in your salads for a flavorful and healthful upgrade.
- Craft vibrant and satisfying salads by pairing romaine with an array of colorful vegetables, lean proteins, and a tasty dressing.
- Romaine lettuce also serves as an excellent foundation for wraps and sandwiches, imparting a crisp texture and nutritional boost to your favorite fillings.
- Experiment with grilling or roasting romaine hearts to unlock unique flavors, or blend them into smoothies for a refreshing twist.
While the recommended daily intake of vegetables is five servings daily, incorporating 2 cups of romaine lettuce into your meals ensures an additional serving in your daily consumption. The versatility of romaine allows you to easily reach your daily vegetable goals, promoting both flavor and well-rounded nutrition.




