
There’s a lot of attention these days on “gut health,” and it seems like there’s a new probiotic supplement or food product infused with live probiotic strains that hits grocery store shelves each week. Even with this rise in popularity and awareness of the importance of the gut microbiome in digestive and overall health, most of us are still conditioned to stay mum about our digestive issues, and keep those struggles or concerns hidden behind bathroom doors.
Because we might live in a society where the tacit undercurrent — at least until very recently — is that we don’t speak about digestion and our gut microbiome in everyday life, many adults aren’t even sure what optimal digestion looks like, what the gut microbiome does or what it even is, and what we should be doing to take care of it besides perhaps something to do with “probiotics,” which is little more than a buzzword that many people know nothing about beyond a vague association with health and the gut.
If this sounds like you, fear not: You’re not alone. Most of us never took a Microbiome 101 course or received instruction about the confusing world of probiotics. Though there probably could be semester-long college courses to cover just the basics of probiotics, we will hit on the key points and need-to-know information to help you learn what probiotics are, what they do, why you might want to take one, and how to pick the right one for your body.
Related Guides
What Are Probiotics?
Probiotics are live, functional microorganisms that improve various functions in your gut and body when taken in adequate amounts. If you imagine your gut microbiome as a garden, probiotics are like seeds or seedlings you plant in your garden of gut microflora to build it out and take up soil space so weeds (pathogens) cannot easily infiltrate and take over.
What Are the Benefits of Probiotics?

In many ways, the benefits of probiotics mimic the beneficial functions of the helpful bacteria residing in your digestive tract because probiotics, at their core, support the gut microbiome.
Bacteria that are beneficial to our health are referred to as commensal bacteria. They perform different functions such as helping digest foods to release the nutrients, fending off viruses and pathogens, promoting cellular repair and turnover, and neutralizing acids and toxins. They support the immune system by fending off pathogenic bacteria by competing for binding sites or real estate, producing various acids and enzymes that make the surrounding environment inhospitable for the pathogens, and signaling the body to produce more white blood cells.
Probiotics help the good bacteria in your gut carry out their various roles, and they make the gut environment less hospitable for pathogenic bacteria. Though not an exhaustive list, there is evidence demonstrating all of the following benefits of probiotics:
- Improving the balance of the microorganisms in your gut.
- Increasing the biodiversity of the microbiota.
- Inhibiting pathogenic colonization of the gut.
- Digesting and absorbing nutrients in the foods you eat.
- Producing certain vitamins, such as B vitamins and K.
- Promoting bowel regularity.
- Supporting the gut barrier to reduce the risk of leaky gut syndrome.
- Reducing the risk of obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and weight gain.
- Helping control normal and abnormal immune and allergic reactions.
- Increasing the turnover of intestinal cells.
- Lowering cholesterol levels.
- Reducing inflammation.
- Improving inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and other digestive issues.
- Attenuating adverse effects of antibiotics on the gut bacteria.
- Improving skin conditions like acne, atopic dermatitis, and rosacea.
- Reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress.
What Are the Side Effects of Probiotics?

Some people may experience some initial digestive distress in response to starting probiotic supplement, but such symptoms should subside within a week or two. If not, or if you experience any moderate or severe discomfort, you should immediately stop taking the supplement and consult your doctor.
Foods Rich In Probiotics

Probiotics can be found in fermented foods. In the absence of oxygen, Lactobacillus bacteria in these foods ferment sugars in the food to lactic acid. The lactic acid in fermented foods is what imparts their tangy or sour flavor. Probiotic-rich foods include the following:
Yogurt

While not all yogurts contain active or live cultures, there are many probiotic-rich yogurts, thanks to the fermenting process where good bacteria like lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria turn milk into yogurt. It’s important to choose organic dairy products to avoid hormones and chemicals, and avoid ones with added sugars.
Kefir

Kefir is a creamy, fermented milk with a slight effervescence. It has been shown to stimulate the immune system and help populate the gut with healthy microbes. It also has antimicrobial properties that allow it to inhibit the growth of pathogens by producing certain acids and alcohols and competing for nutrients.
Sauerkraut

Sauerkraut is a preserved and salted cabbage slaw that has been shown to improve GI symptoms and support the gut microbiome. Skip the pasteurized options though; the live probiotics are only present in the raw and unpasteurized form.
Kimchi

Kimchi is a brined, salted, fermented, spicy cabbage and vegetable slaw that originates in Korea. It has been shown to help populate the gut microbiome with healthy microbes, reduce inflammation, and improve digestion.
Sourdough Bread

A fermented starter made from lactic acid bacteria and yeast is used to make sourdough bread. Consuming sourdough bread has been shown to impart favorable changes to the gut microbiota populations.
Tempeh
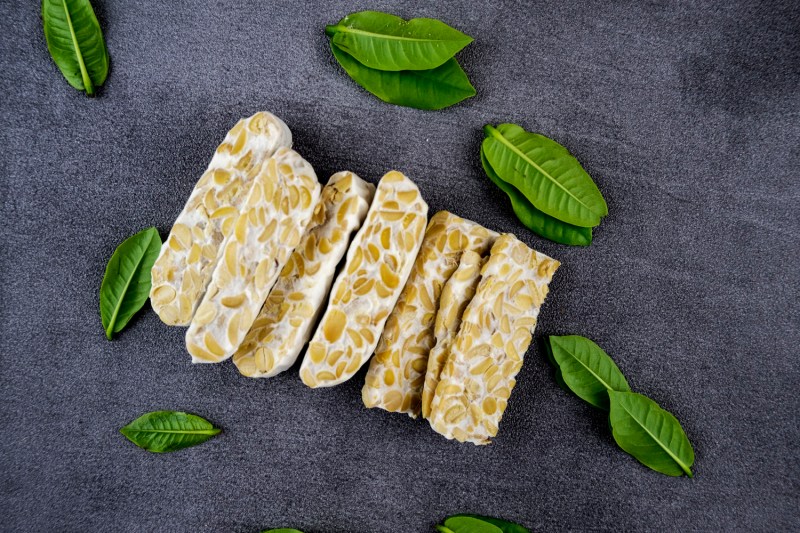

Tempeh is a fermented soy product with a slightly nutty, umami taste. The fermenting process increases the bioavailability of some of the nutrients in the soybeans and reduces the anti-nutritive effects of the phytic acid. There is evidence to suggest it has anti-inflammatory and gut-supporting properties.
Natto
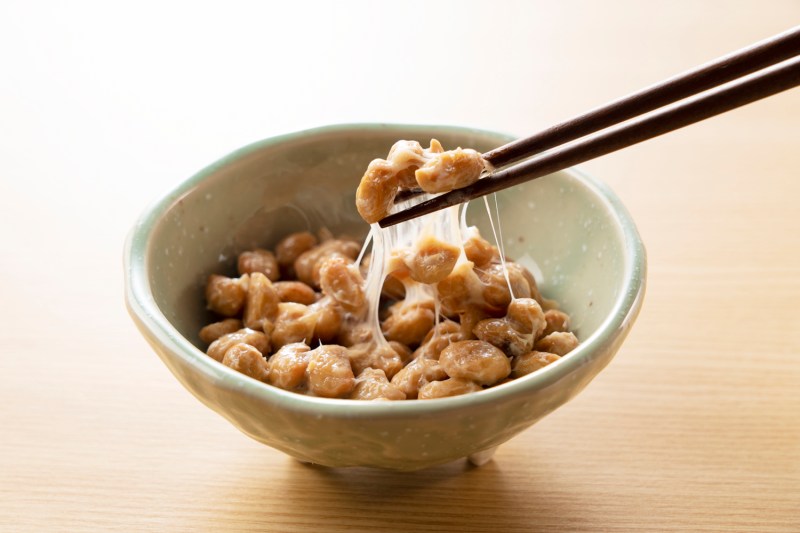

Natto is a sticky, fermented soybean product with a funky smell and taste. It’s very high in vitamin K2 and contains a bacterial strain called Bacillus subtilis.
Kombucha
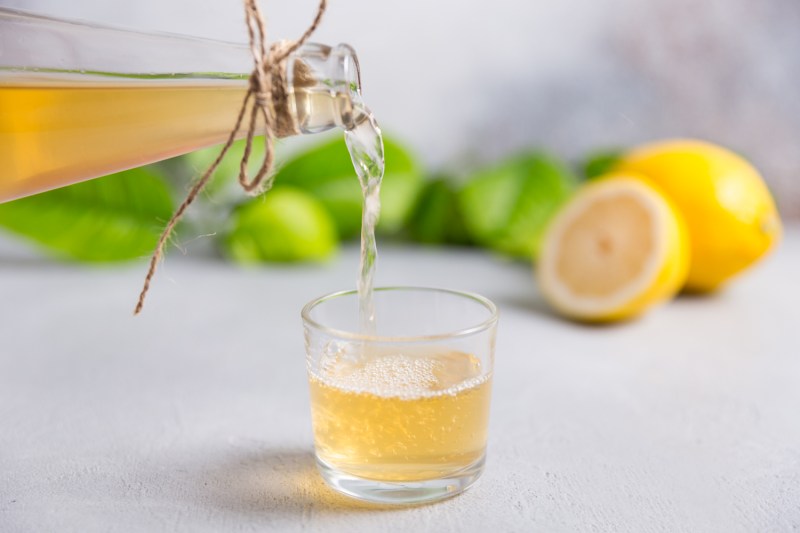

Kombucha is black or green tea fermented with bacteria and yeast that can help lower blood sugar levels.
Certain cheeses, pickles, buttermilk, miso, and raw milk can also naturally contain probiotics and functional organisms.
Probiotic Supplements

There are tons of probiotic supplements on the market today, with new ones seemingly added weekly. Trying to pick the best one for you can quickly become incredibly overwhelming. Though there are a variety of specific strains you’ll find listed on different probiotic supplements, most fall into the Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus genera. A probiotic supplement that contains a blend of different species is usually preferable to help provide the broadest swath of benefits.
Supplements that contain live bacterial strains typically require refrigeration, while spore-based probiotics are shelf-stable. There is evidence supporting the efficacy of both types. Unless directed otherwise, most probiotics should be taken daily — rather than sporadically — to maximize their effectiveness.



